The falx cerebri attaches to the frontal bone at the frontal crest and at the sulcus of the superior longitudinal sinus
 Dura Mater: Osseus attachements of the dura duplications:
Dura Mater: Osseus attachements of the dura duplications:
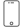
Anterior inferior the falx cerebri is attached to the ethmoid bone’s Crista galli.
The falx cerebri attaches to the frontal bone at the frontal crest and at the sulcus of the superior longitudinal sinus.
On the parietal bone its attachments are on both sides at the sulcus of the superior longitudinal sinus.
 At the occipital bone it attaches at the sulcus of the superior longitudinal sinus and at the internal occipital protuberance.
At the occipital bone it attaches at the sulcus of the superior longitudinal sinus and at the internal occipital protuberance.
The tentorium cerebelli attaches at the internal occipital protuberance and at the sulcus of the lateral sinus of the occipital bone.
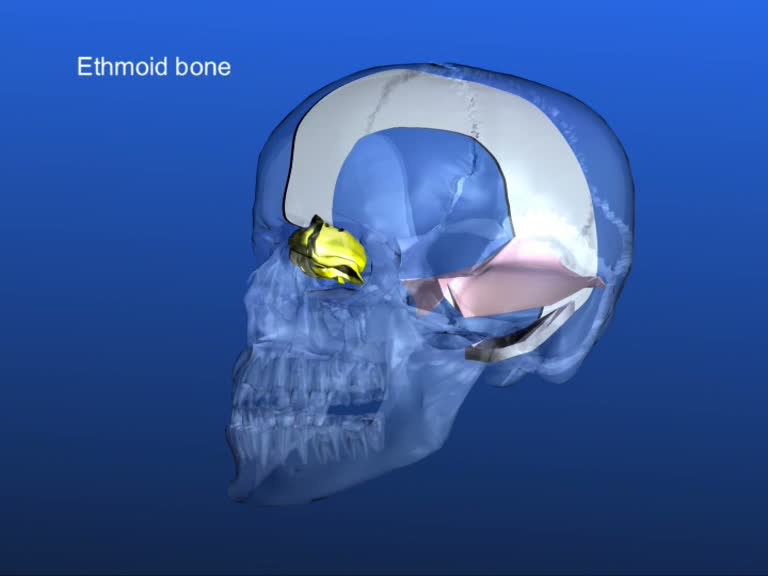
It runs laterally along the little parieto-mastoid suture and attaches there with its upper layer, at the lower posterior angle of the parietal bone, while its lower attachment is located at the mastoid portion of the temporal bone. Dysfunctions can easily occur at this place.
Further along, the tentorium is attached at the margo superior of the petrous portion of the temporal bone.
In the front, the lateral parts of the tentorium are attached at the two posterior clinoid processes of the body of the sphenoid. The internal edges (rims, boarders) of the tentorium continue anterior, cross the anterior lower layers of the tentorium and are attached at the anterior clinoid processes of the lesser wings. The trochlearis nerve lies at the point where the internal part of the tentorium crosses the external part. It can be disturbed through abnormal tensions or ossifications of the dural attachments.