The tentorium cerebelli devides the cerebellum from the cerebrum and extends like a tent over the cerebellum.
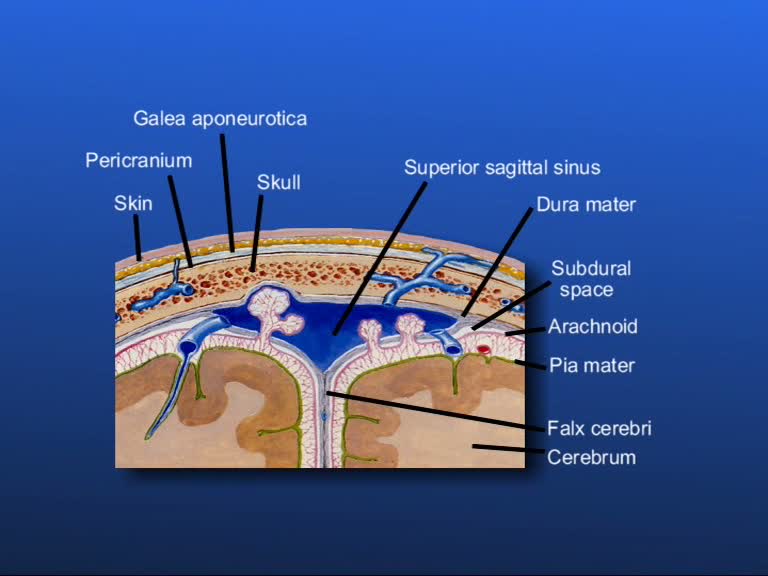
The formation of the meninges:
Here you see the formation of the meninges: the dura mater on the outside, the arachnoid in the middle and the pia mater on the inside. The outer meninx, the dura mater, consists of compact, uneven and very tough connective tissue with many collagenic (fibrous) fibers. There are several places in the skull where the meningeal dura folds inward, so that cavities are formed for the venous vessels, as for example in this case the superior sagittal sinus. Dura duplications, that are as thick as a fingernail, are formed: The falx cerebri, the falx cerebelli and the tentorium cerebelli.
The falx cerebri divides the two hemispheres from each other. The tentorium cerebelli devides the cerebellum from the cerebrum and extends like a tent over the cerebellum. The falx cerebelli divides the two halves of the cerebellum.
The structure of the fibre forms through the forces that have an influence on the dura.
<