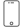
The osteopath supports one of the two structures (for ex. The hyoid) and brings it to a point of balcance
 Palpatory differential diagnosis of the dysfunctional level:
Palpatory differential diagnosis of the dysfunctional level:
The osteopath differentiates whether the restricted movement and hardened tissue originates from the bone, from the dura, from brain tissue or from the fluids. A resonance could also be made with electromagnetic fields.
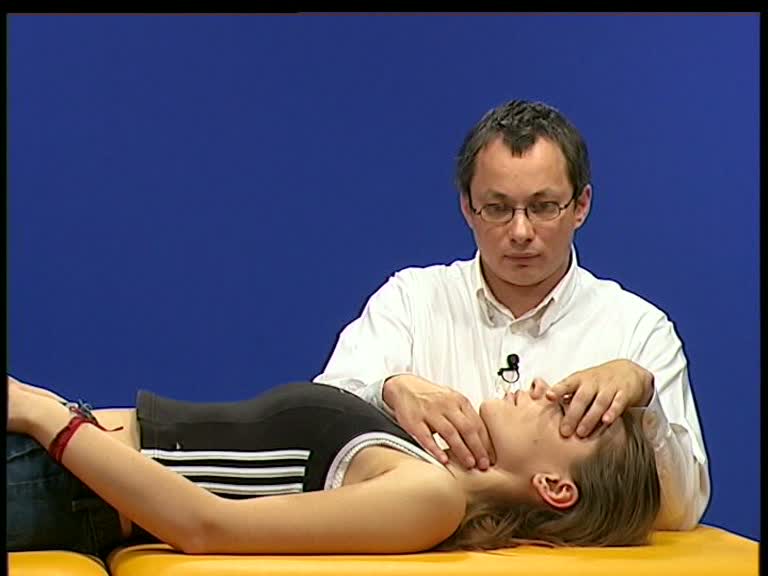 Diagnostics: Palpatory differential diagnosis:
Diagnostics: Palpatory differential diagnosis:
With the following differential diagnosis it is possible to examine whether the movement restriction of a certain structure (for example spenobasilar synchondrosis) is caused by a different tissue of the body (for ex. The Hyoid).
The osteopath supports one of the two structures (for ex. The hyoid) and brings it to a point of balcance.
After that he examines, whether the inherent movement or mobility at the sphenobasilar synchondrosis has changed. A normalisation or improvement suggests that the hyoid bone has restricted the sphenobasilar synchondrosis.
A decrease in movement or mobility suggests that the sphenobasilar synchondrosis has used the hyoid bone as a compensation.